General Right Triangles
General Explanation
In an earlier lesson we learned that the measure of a right angle is 90 degrees.
A RIGHT TRIANGLE is a triangle that has one right angle. The two sides closest to the right angle are called the LEGS. The side opposite the right angle is called the HYPOTENUSE.
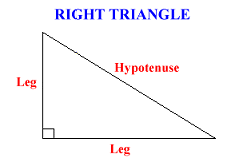
The measures of the three angles of any triangle add to 180 degrees. A right triangle contains two acute angles and a right angle. The two acute angles add to 90 degrees, and so they are complementary. There is an important relationship between the legs and the hypotenuse in a right triangle. It is called the PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM. To understand the Pythagorean Theorem, let a and b stand for the lengths of the two legs, and let c stand for the length of the hypotenuse. 
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the measure of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the measures of the two legs. 
We can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find any side of a right triangle when we are given the lengths of the other two sides. Sample Problem 1
In a right triangle we are given the lengths of the two legs. a = 5 and b = 12.
Find the value of c, the length of the hypotenuse.
Solution
We will use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of c.
c2 = a2 + b2
c2 = 52 + 122
c2 = 169
c =
√ 169 = 13
Sample Problem 2
In a right triangle we are given the lengths of the hypotenuse and one of the legs.
c = 10 and a = 4. Find the length of the other leg (side b) to 2 decimal places. Solution
We will use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of b.
c2 = a2 + b2
102 = 42 + b2
100 = 16 + b2
84 = b2
b =
√ 84 = 9.17
|


